Emerging Innovations and Trends Shaping the Future of Healthcare
Written By: Beata Faitli
Published on: 04.04.2025
The healthcare industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by groundbreaking innovations and emerging trends. These changes are redefining how patient care is delivered, making it more efficient, effective, and personalized. This article explores the latest advancements in telemedicine, wearable technology, personalized medicine, and AI-driven diagnostics, highlighting their impact on the future of healthcare.
Transformative Technologies Within Healthcare
Telemedicine
Telemedicine has significantly transformed the landscape of healthcare delivery by enabling remote consultations and care management. This innovation allows patients to connect with healthcare providers via video calls, phone calls, or messaging, ensuring continuous care without the need for travel. The convenience and accessibility of telemedicine are particularly beneficial for patients in remote or underserved areas, as well as for those with mobility challenges. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine proved essential in maintaining healthcare access while minimizing the risk of virus transmission, showcasing its effectiveness and potential for long-term integration into healthcare systems (NHS Digital).
Moreover, telemedicine has been instrumental in mental health care, where continuity and ease of access are crucial. Online therapy sessions and digital psychiatric assessments have become more commonplace, providing necessary support while preserving patient privacy and comfort. Additionally, telemedicine facilitates the management of chronic diseases by enabling regular follow-up appointments and real-time adjustments to treatment plans based on patient-reported data, all from the patient’s home.
The future of telemedicine looks promising as integration with AI and machine learning continues to evolve, enhancing the capabilities of virtual care platforms. These technologies can improve the accuracy of remote diagnoses and patient monitoring, further revolutionizing how care is delivered. The ongoing development of telemedicine infrastructure, backed by policy support and technological advancements, is likely to cement its role as a cornerstone of modern healthcare delivery.
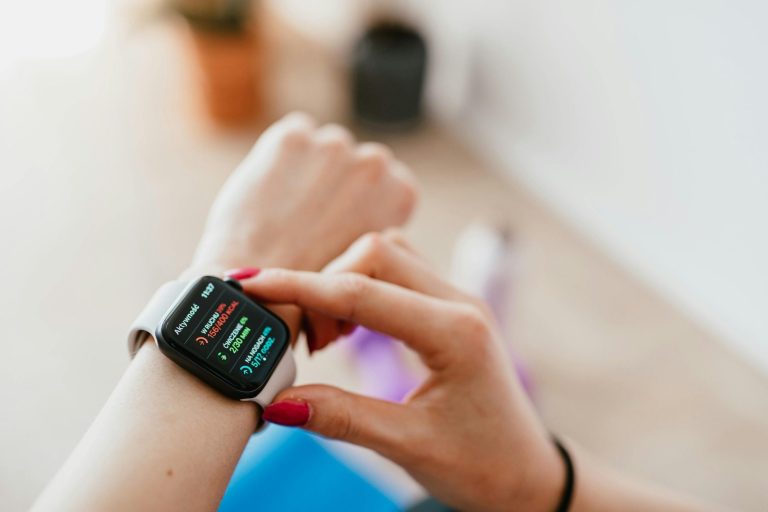
Wearable Technology
Wearable technology has become a key player in proactive health management, extending its capabilities beyond fitness tracking to include advanced health monitoring features. Devices such as smartwatches and fitness bands are equipped with sensors that track cardiovascular health, sleep quality, and even stress levels, providing users with comprehensive insights into their well-being. These devices encourage a more active role in personal health management, fostering a culture of health awareness and preventive care (NHSX).
The data collected by wearable devices are increasingly used by healthcare professionals to supplement traditional clinical diagnostics. For instance, wearable technology can continuously monitor heart rhythms and alert users and their doctors to irregularities, potentially identifying heart conditions like atrial fibrillation before they lead to more serious complications. This real-time monitoring can be life-saving and significantly alters the management strategies for chronic diseases.
Looking ahead, the integration of wearables with telehealth services is expanding the reach of remote monitoring programs, which can significantly impact patient outcomes, especially for chronic disease populations. The continuous evolution in wearable technology promises even greater integration into medical diagnostics, therapy delivery, and personalized medicine, driven by ongoing advancements in sensor technology and data analytics.

Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is at the forefront of a healthcare revolution, driven by advancements in genomic medicine and big data analytics. This approach shifts the one-size-fits-all paradigm of traditional medicine to more tailored treatments that consider individual differences in people’s genes, environments, and lifestyles. By analyzing a patient’s genetic profile, clinicians can predict more accurately which treatments and prevention strategies will be effective for specific individuals, reducing trial and error and improving outcomes (Genomics England).
This tailored approach is particularly transformative in oncology, where genetic information guides the use of targeted therapies that attack cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue, improving treatment efficacy and reducing side effects. Beyond oncology, personalized medicine is making strides in areas such as pharmacogenomics, where genetic information is used to predict an individual’s response to drugs, including antidepressants and anticoagulants.
The growth of personalized medicine is facilitated by the decreasing cost of genomic sequencing and the increased availability of big data computational tools. These advancements ensure that personalized medicine will continue to expand its impact, offering more patients tailored and effective care options.
AI-Driven Diagnostics
AI-driven diagnostics are changing the face of healthcare by enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of medical assessments. AI algorithms excel in pattern recognition, making them particularly useful in fields like radiology and pathology where diagnostic accuracy is crucial. These tools can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, faster and often more accurately than human eyes, identifying early signs of diseases such as cancer, which might be missed otherwise (Health Data Research UK).
AI also plays a crucial role in predictive diagnostics, where it helps in anticipating disease progression and patient outcomes. This aspect of AI is essential for planning treatment paths and managing healthcare resources effectively, particularly in chronic disease management. Moreover, AI tools are being employed in emergency rooms where they assist in triaging patients based on severity, improving response times and patient outcomes.
As AI technologies continue to evolve, their integration into daily clinical practice is expected to grow, supported by improvements in AI algorithms, increased data availability, and more robust computing power. This trend promises to enhance diagnostic processes across multiple areas of medicine, making healthcare delivery more precise, personalized, and efficient.
Further Innovations in Healthcare
3D Printing
3D printing is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling the production of customized prosthetics, implants, and even bioprinted tissues. This technology allows for the creation of patient-specific devices that enhance comfort and functionality, significantly improving patient outcomes. For example, 3D-printed prosthetics can be tailored to an individual's anatomy, providing a more personalized fit and reducing the time and cost associated with traditional manufacturing methods. In orthopedics, 3D printing is used to produce customized implants that match the exact shape of a patient's bone, facilitating better integration and faster recovery.
Moreover, bioprinting—an advanced form of 3D printing—holds the potential to create living tissues and organs. This innovation could address the shortage of organ donations, providing patients with life-saving solutions. While still in the experimental stages, bioprinted tissues are being used for drug testing and research, reducing the need for animal models and expediting the development of new treatments. As 3D printing technology continues to advance, its applications in healthcare are expected to expand, offering even more personalized and effective solutions for patients (NHS England).
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is making significant inroads in healthcare by enhancing data security and interoperability. By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain ensures that healthcare records are securely stored and transparently shared among authorized users. This technology addresses critical issues related to data breaches and privacy, offering a robust solution for safeguarding sensitive patient information. Blockchain's transparency also facilitates trust among patients and healthcare providers, as it allows patients to have control over who accesses their data.
In addition to security, blockchain promotes interoperability by enabling seamless data exchange across different healthcare systems. This interoperability is crucial for improving care coordination, as it ensures that healthcare providers have access to accurate and up-to-date patient information. By reducing data silos and streamlining information sharing, blockchain can enhance clinical decision-making and improve patient outcomes. As more healthcare organizations adopt blockchain, it is poised to play a pivotal role in transforming healthcare data management (Health Data Research UK).
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is at the forefront of minimally invasive procedures, offering greater precision and control to surgeons. This technology allows for complex operations to be performed through small incisions, reducing trauma to the body and resulting in quicker recovery times for patients. Robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, provide surgeons with enhanced visualization and dexterity, enabling them to perform delicate procedures with high accuracy. The precision of robotic surgery minimizes complications and improves surgical outcomes, particularly in fields like urology, gynecology, and cardiothoracic surgery.
Patients undergoing robotic surgery often experience less pain, reduced blood loss, and shorter hospital stays compared to traditional open surgeries. These benefits not only enhance patient satisfaction but also reduce healthcare costs by decreasing the need for postoperative care and rehabilitation. As technology continues to evolve, robotic surgery is expanding its applications to include more complex procedures, making it a valuable tool in modern surgical practice (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence - NICE).
Virtual Reality (VR) Therapy
Virtual Reality (VR) therapy is an innovative tool in healthcare, offering immersive therapeutic experiences for pain management, rehabilitation, and mental health treatments. By creating realistic simulations, VR can distract patients from pain and discomfort, reducing their reliance on medication. In rehabilitation, VR is used to create engaging and interactive environments that motivate patients to perform physical exercises, enhancing recovery outcomes. For mental health, VR provides exposure therapy in a controlled and safe setting, helping patients confront phobias, anxiety, and PTSD.
The immersive nature of VR allows for personalized therapy sessions tailored to individual patient needs, making treatment more effective. VR also offers the advantage of remote therapy sessions, providing access to care for patients who may be unable to attend in-person sessions. As VR technology becomes more accessible and affordable, its applications in healthcare are expected to grow, offering innovative solutions for a wide range of therapeutic needs (NHSX).
Voice Assistants and AI Chatbots
Voice assistants and AI chatbots are increasingly being utilized in healthcare to enhance patient engagement and streamline administrative tasks. These tools provide patients with immediate access to health information and support, answering questions about symptoms, medications, and treatment plans. By offering 24/7 assistance, chatbots improve patient satisfaction and reduce the burden on healthcare staff, allowing them to focus on more complex patient interactions. In addition, voice assistants can be integrated into healthcare systems to facilitate appointment scheduling, medication reminders, and care plan adherence, enhancing overall patient management.
The use of AI in these applications ensures that interactions are personalized and relevant, improving the patient experience. Moreover, the data collected through these interactions can be analyzed to identify trends and improve healthcare delivery. As AI technology advances, voice assistants and chatbots are expected to play an even greater role in healthcare, supporting both patients and providers in delivering efficient and effective care (NHS Digital).


Conclusion
The rapid advancements in healthcare technology, from telemedicine to AI-driven diagnostics, are reshaping the landscape of patient care. These innovations not only enhance the efficiency and accessibility of healthcare services but also pave the way for more personalized and effective treatments.
As wearable technology, personalized medicine, and emerging tools like 3D printing and blockchain continue to evolve, they promise to transform healthcare into a more patient-centered and technologically advanced system. Embracing these trends will be crucial for healthcare providers to improve outcomes and meet the growing demands of modern healthcare.
Enjoyed this article? Share it on social media and spread the knowledge!
REFERENCES
- NHS England - https://www.england.nhs.uk
- Health Data Research UK - https://www.hdruk.ac.uk
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) - https://www.nice.org.uk
- NHSX - https://www.nhsx.nhs.uk
- NHS Digital - https://digital.nhs.uk
Website Image sources:
Pexels - https://www.pexels.com/ and Pixabay - https://pixabay.com/
ChatGPT/Dall-E generated images
Interested in learning how these insights can apply to your organization?
Book a consultation today to discover how I can deliver actionable insights to drive your success!

Join the "Quiet Numbers, Loud Impact" newsletter
Join “Quiet Numbers, Loud Impact” to get new free and low-cost resources — designed to help small charities and care teams use their data more meaningfully.
